Ink Ready Dispersions – IRDs
Building on our parent company’s expertise in color and our own specialization in surface treatments, Shepherd Technologies (ST) has created a CMYK set of low-migration, heat-stable, high-loading inorganic color dispersions suitable for digital printing and thin films systems (Figure 1). We call the products ink ready dispersions (IRDs).
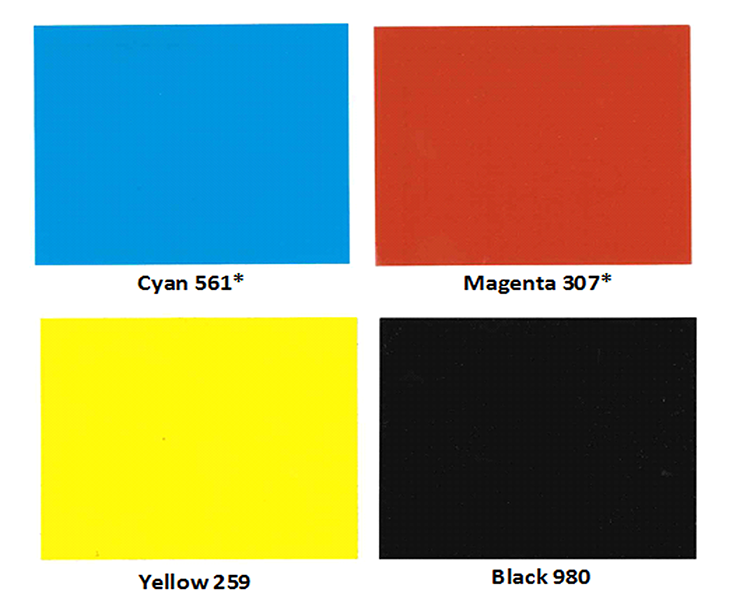

Figure 1. CMYK set of IRDs
*Colors achieved using white + color ink
Key Features and Benefits When Using IRDs in Digital Inks and Films
Inorganic pigments in IRDs provide the following benefits over traditional printing ink pigments and dispersions:
- Non- migrating, non-bleeding colors
- > 90 % color pigment
- Easy dispersion
- Greater visual opacity
- Superior UV/fade resistance
- Good chemical resistance
- Unique infrared signatures
- Excellent heat resistance
IRDs are inorganic pigment preparations. Delivered as dry powder, high loading dispersions, they contain over 90 % inorganic color pigment. The high pigment loading allows for use in a variety of ink and film systems.
Digital inks made with IRDs can be used alone or in combination with organic inks. They can be formulated using typical ink preparation methods.
Easy Dispersion of IRDs
The normally difficult-to-disperse inorganic pigments in IRDs are formatted to readily disperse to digital size in a manner similar to that used in the preparation of organic pigmented inks. A chart detailing the particle size of the dry IRD before dispersing into an ink, and after, is shown in Figure 2.
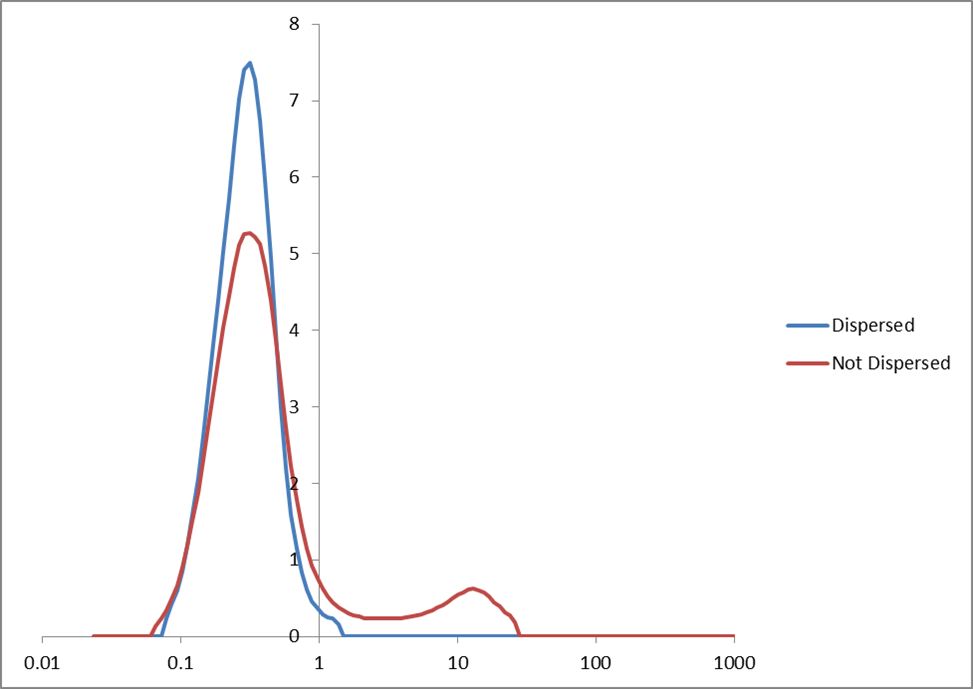
Figure 2. Laser light scattering particle size (microns) of pigment in an IRD before and after ink preparation.
IRD milled particle size: Mean ~ 0.3μ, D99 < 1.2μ
Applications, Suitability and Suggested Uses
IRDs are suitable for water based, solvent based, and UV/LED inks. They can also be used in silicone-based thin coating systems. Some but not all are suitable for chemically demanding sol-gel coatings and as colorants for digital glass and ceramic inks. A compatibility chart is shown in Figure 3.
Print heads such as those offered by Xaar and Konica-Minolta are commonly used with inorganic digital ink applications.
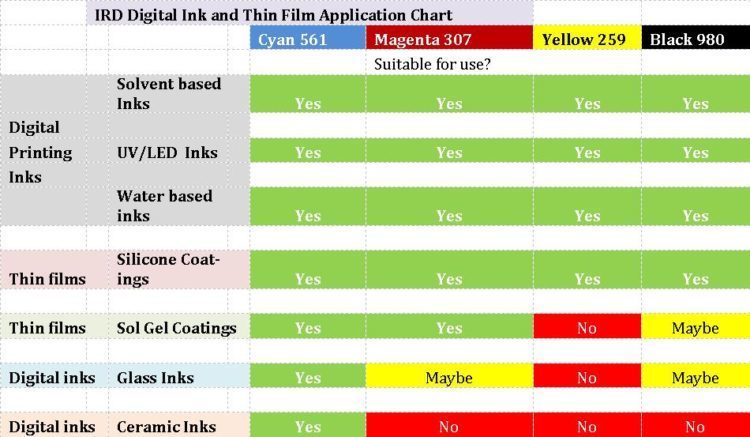
Figure 3. IRD application and suitability chart.
Digital printing examples using a CMYK set of IRD-based inks
Figures 4 to 7 are examples of digital images made using IRDs as color in LED cured inks. Inks were made by dispersing all four IRDs as separate CMYK inks.
LED wide format ink
Sand mill dispersion
Printed images made with Konica-Minolta 1024i print heads
C – ink made with 3 % Blue 561, 0.3 % Blue 15:3**
M – ink made with 1.5 % Magenta 307
Y – ink made with 2.5 % Yellow 259
K – ink made with 2.5 % Black 980
**note: C ink was not chromatic enough on its own in this evaluation to produce good 4-color images. It was necessary to add 0.3 % of organic ink to make the color suitable for four color printing.

Figure 4. Digitally printed image of color ribbons using IRD based inks
Figure 5. Digitally printed image of color spectrum using IRD based inks

Figure 6. Digitally printed image of patio bricks using IRD based inks

Figure 7. Digitally printed image of wood panels using IRD based inks
